Big Data is opening up a whole new world for manufacturers. Moreover, Big Data has become an important element of ERP system with the ability to link all data to people and processes.
Read more: Data Lake vs. Data Warehouse
That is the reason why there are more and more manufacturers realising the value of Big Data and investing money in it. In 2015, the Tech Target IT Priorities Survey showed that 31% of worldwide respondents (the total was 2,212) said their organisations had plans to use BI, analytics, or data warehousing tools for running a business. Besides, 25% of them were looking forward to investing in Big Data analytics, and 21% hoped for money for Big Data processing and management.
In a report done recently by Pierfrancesco Manenti, 47% of manufacturers hope to see Big Data analytics’ huge impact on their enterprises’ performance; and 49% believe that advanced analytics can reduce expenses and utilise resources.
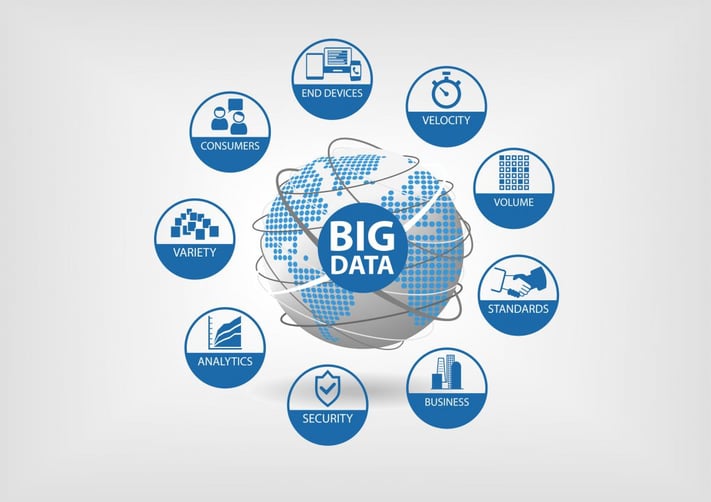

Data’s sources in Big Data analysis
Data is the core of Big Data, and can be collected from external and internal sources, or generated by the machine-to-machine method.
- External sources: User groups or forums, social media channels, focus groups, or surveys.
- Internal sources: Enterprise’s own systems, like ERP, CRM, etc.
- Machine-to-machine method: Smart sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT) can take data directly from machines and equipment, and send it on to an ERP and EAM systems, or other applications.
Read more: Data Analytics at a Hyper Speed with Tableau 10.5
How can Big Data help?
In Big Data analysis, data can be used to identify and study business opportunities by helping manufacturers:
- Identify new opportunities: by matching demographics of the current customers with profiles of potential ones in other regions, or countries, to simplify the global expansion.
- Expand into new markets: by spotting hidden opportunities, identifying niche/micro-markets, therefore, becoming trusted advisors and gaining competitive advantages.
- Make plans on a customer base: by identifying opportunities for selling to current customers, predicting the customer needs, reinforcing the organisation’s message, as well as demonstrating the value of various kinds of product.
- Nurture relationship with customers: by understanding customer needs to provide creative solutions and build strong bonds with them.
Read more: Rise of the CDO (Chief Data Officer) and the Growing Importance of Data
- Innovate: by using data to predict the impact of design or engineering refinements, speed up the product innovation process or the launches of breakthrough solutions, and accurately forecast a new product’s impact on sales or risks.
- Improve product lifecycle: by identifying flaws and weak points to refine product features, sorting out efficient suppliers and sub-contractors, and eliminating poorly performing sub-contractors.
- Raise added value: by extending offerings to enhance the customer experience and the value-add, and managing them with greater efficiency.
- Get more profit: by optimising the lean initiatives to reduce waste, improve productivity, and stretch out the thin margins.
 English
English  Vietnamese
Vietnamese 


