ERP accounts for the largest share of enterprise software spending. According to Gartner's Market Share, ERP software revenue increased globally by 11% from 2020 to 2021, reaching a total of $44.4 billion.
Contents
- 2022 Gartner’s Magic Quadrant explained
- Highlights of the strengths and cautions of Gartner’s cloud ERP leaders
About 47% of the ERP market's revenue today comes from on-premises ERP offerings and 53% from cloud ERP offerings. It is expected that, by 2024, over 60% of product-centric enterprises will employ cloud ERP platforms, and at least half of existing ERP mega customers will employ multiple vendors.
Cloud ERP for product-centric enterprises supports automation in operational and financial processes for the manufacturing, distribution, delivery, and servicing of goods.
The core features of a typical product-centric cloud ERP suite include operational ERP and financial management. Features like procurement, human capital management (HCM), and industry-specific modules or applications are optional to add depending on the needs of each business.
Read more: Here’s What You Need to Know About Top ERP Vendors
2022 Gartner’s Magic Quadrant explained
The Magic Quadrant is a series of market research reports published annually by the Stamford-based IT consulting firm Gartner. The report uses proprietary qualitative data analysis methods to provide insights into a particular technology, market trends, providers’ capabilities, and suitability for organisation needs, thus easing the process of solution research and selection.
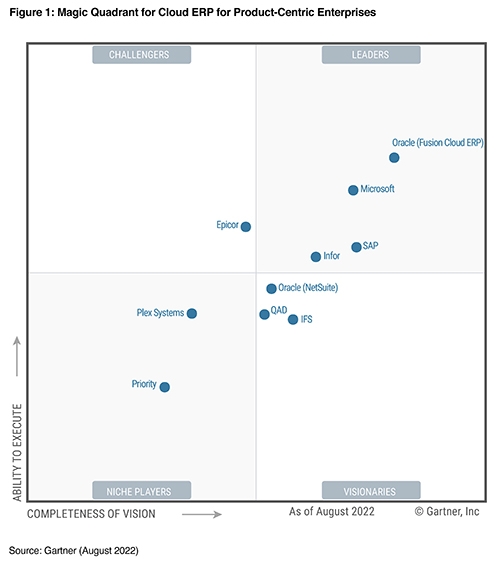
Figure 1: Magic Quadrant for Cloud ERP for Product-Centric Enterprises (Source: Gartner 2022)
A Magic Quadrant report typically categorises technology providers into four types:
- Leaders: have a market-defining vision and the capacity to function in all business sizes and markets with a vast network of system integrator partners.
- Challenger: have a bigger market share compared to Niche Players and Visionaries; offer reliable and effective cloud services but lack the vision to execute in larger markets consistently, and thus only concentrate on particular business size.
- Visionaries: have a good technological and functional vision, suitable for organisations that seek to implement ERP product-centric systems quickly. Their downside is limited execution or track record.
- Niche Players: target different industry segments or company sizes but have limited visions and execution capabilities.
Gartner's list of Magic Quadrant vendors may vary over time, but the report has a limit of 20 providers. Each of them is evaluated based on Gartner's two key criteria and is expected to satisfy core capabilities as well as requirements for market presence and cloud service attributes.
Read more: Everything You Need to Know About Cloud ERP in 10 Minutes
Highlights of the strengths and cautions of Gartner’s cloud ERP leaders
Infor (Infor CloudSuites)
Infor has been named a leader consistently for several consecutive years.
Infor is known for having vertical-specific and user-centric solutions. Recently, the company has invested immensely in more cloud-based solutions for its new and existing customers. Today, it has broadened its offerings to include multitenant cloud solutions.
Their Infor CloudSuites have several distinct solutions, each featuring separate core functionalities to cater to different verticals and business sizes. For instance, SyteLine is suitable for small-to-midsize manufacturers, while Infor LN is for large and global discrete manufacturing.
All in all, Infor's cloud ERP solutions are flexible to meet the demands for robust operational processes and manufacturing capabilities, particularly in industrial equipment, automotive, aerospace, defence, consumer goods, food and beverage, fashion, and wholesale distribution sectors.
Strengths
- Expand and integrate CloudSuites through Infor OS: the Infor OS enterprise application platform offers a low-code capability to extend and interface with numerous Infor products and other cloud-based and on-premises solutions.
- Support complicated manufacturing scenarios: has a strong capacity to support process, project, "X-to-order," and asset-intensive manufacturing.
- Industry-specific capabilities: out-of-the-box solution with vertical-specific and last-mile functionality and content to support complex industries.
Cautions
- Though improved, Infor's technical product support does not consistently meet the high level required of a cloud SaaS provider.
- Compared to other leaders in the quadrant, Infor has fewer application service partners to support its worldwide expansion. However, Infor has established connections with a number of international system integrators.
- Licensing and contracting can be difficult if a company has multiple business lines.
Read more: An Overview of End-to-End ERP System Infor CloudSuite Industrial
Microsoft
Microsoft is an integrated ERP solution combining two distinct but interconnected solutions—Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. Microsoft typically targets medium and large businesses, but its solutions are also suited for multinational corporations that require highly specialised regional and industry competencies.
Strengths
- Consistent cloud and platform approach: Running on the Microsoft Azure cloud, users can utilise a wide range of features, such as the Microsoft Power Platform for analytics through Power BI, low-code extensions through Power Apps, data management via Dataverse, and hyper-automation through Power Automate.
- Endless expansion: with more than 5,000 extensibility points, Microsoft Dynamics 365 enables customers to innovate their business processes beyond the core standard modules while ensuring integrity remains intact whenever a new Microsoft release comes out.
- Increased adoption and diverse offerings: Microsoft Dynamic 365's customers, including large enterprises, continue to rapidly grow. The solution is being positioned as the leading software for complex and international enterprises needing specific localisations when adopting a two-tier or multiple-tier ERP strategy.
Cautions
- Support for complex manufacturing requirements: despite the increased adoption by large, complex enterprises, Gartner's discussion with Microsoft users shows concern if the solution can meet their requirements.
- Financial capabilities: compared to our vendors that target large and global scale businesses, Microsoft Dynamic 365 is weaker in this area and has limited financial closing and planning capabilities.
- Implementation quality: Microsoft relies on its vast network of resellers and ISVs to reach customers, which can lead to quality discrepancies and varying implementation services when integrating non-Microsoft products.
Oracle (Fusion Cloud ERP)
Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP offers multiple operational, administrative, and logistical ERP features for upper-midsize, large, and international businesses.
Strengths
- A wide range of features: including discrete and complex manufacturing, distribution, finance, procurement, and human capital management.
- Global scope and reach: particularly designed for large, multinational enterprises with a sizable global network of implementation partners as well as multi-language, multi-currency, and regulatory support in most countries.
- Embedded AI, ML, and analytics capabilities: the solution's single data model combining embedded AI, ML, and analytics capabilities provides both automation and real-time data, enabling users to make more informed decisions.
Cautions
- Complex installation and support: despite providing a wide range of features, it is challenging to get the solution up and running and maintain it due to the complexity of the features.
- Integration difficulties: challenges arise when integrating Oracle Fusion Cloud ERP with customers' current on-premises or cloud solutions.
- User interface: Oracle is striving to enhance the UX of its entire application portfolio to meet the increasing customer desire for better module navigation, search functionality, and mobile experience.
SAP (SAP S/4HANA Cloud)
If what organisations are looking for is a solution to their complex supply chain, manufacturing, and financial business operations, SAP S/4HANA Cloud might be the answer.
Read more: SAP vs Infor - Software Giants Face Off Over Cloud Strategy
Strengths
- Enterprise and industry expertise: SAP S/4HANA Cloud has tremendous experience with large international corporations and specific industries. SAP's recent cloud offering, Industry Cloud, is expected to provide specific industries with a broader range of SAP and non-SAP capabilities to function alongside SAP S/4HANA Cloud.
- Technology platform capabilities: used together Business Technology Platform has allowed its customers to leverage a range of services, including data analytics, AI/ML, process automation, and application development.
- Analytics: built-in capabilities for its ERP and dependent products help SAP meet more demands, such as serving supply chain planning, extended planning and analysis, and data visualisation.
Cautions
- Deployment options: compared to other vendors, SAP S/4HANA Cloud has a low adoption rate. As SAP has different capabilities among different deployment options, customers are confused about the best way to adopt SAP ERP. It is challenging to compare prices since these deployment choices have so many distinct licenses and pricing options.
- Difficulties for current clients: Many long-standing SAP ERP clients are still debating whether to switch to SAP S/4HANA, and S/4HANA Cloud has only been adopted by clients longing to carry out significant digital transformation plans.
- Support: clients typically view SAP as an expensive vendor and give SAP poor ratings for its overall service, the calibre of its technical help, and the overall success of its contract negotiations.
Subscribe to our TRG Blog or download our whitepaper below to learn more about this comprehensive, all-in-one solution!

 English
English  Vietnamese
Vietnamese 

